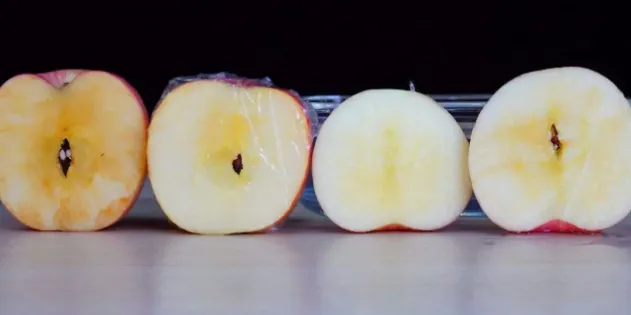
In life, we often see that the flesh of cut apples will slowly turn from white to yellowish brown after being oxidized in the air. In fact, this oxidation also occurs in our human body. The human body continues to generate free radicals in the human body due to continuous contact with the outside world, including respiration (oxidation reaction), metabolism, external pollution, radiation exposure and other factors.
The production of an appropriate amount of free radicals not only provides and delivers energy for cells to maintain life activities, but is also the initiator and regulator of various metabolism and signaling pathways in our body; the impact of excessive free radicals on the human body can range from loose and dark skin to If it is yellow, it will accelerate aging; in severe cases, it may cause cancer or other diseases.
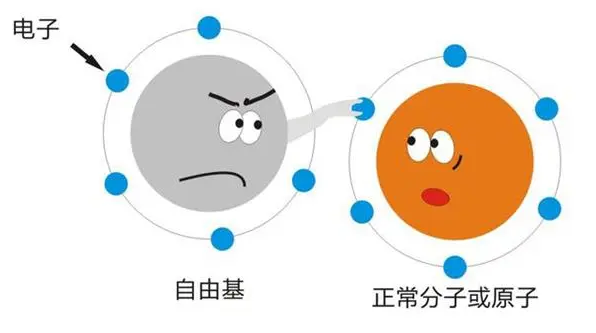
Research on antioxidants can effectively overcome the harm caused by excessive free radicals. Therefore, antioxidants are not only the main research and development direction of health care products and cosmetics companies, but also an important functional demand in the market. Among them, glutathione is one of the important research products.
Glutathione
As an important intracellular metabolism-regulating and antioxidant substance, glutathione is not only the prosthetic group of glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase, but also the coenzyme of glyoxalase and triose dehydrogenase. It participates in the production of tricarboxylic acid in the body. Circulation and sugar metabolism, and can activate a variety of enzymes, such as sulfhydryl (SH) enzyme-coenzyme, etc., thus promoting the metabolism of sugar, fat and protein. The GSH molecule is characterized by having an active sulfhydryl group (-SH), which is the most important functional group. It can participate in a variety of important biochemical reactions in the body, protect the sulfhydryl groups of important enzyme proteins in the body from oxidation and inactivation, and ensure energy metabolism and cell utilization. At the same time, it combines with free radicals in the body through sulfhydryl groups, which can directly reduce free radicals into acidic substances, thereby accelerating the excretion of free radicals and combating the damage of free radicals to important organs.
Part.1
In 2009, a foreign research team published an article in "Antioxid Redox Signal". Describes the key role of mitochondrial glutathione in antioxidants.

Mitochondria are the major intracellular site of oxygen consumption and the major source of reactive oxygen species (ROS), most of which come from the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Among the arsenal of antioxidants and detoxifying enzymes present in mitochondria, mitochondrial glutathione (mGSH) emerges as the primary line of defense in maintaining a proper mitochondrial redox environment to avoid or repair oxidative modifications that lead to mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death. The importance of mGSH lies not only in its abundance but also in its versatility to counteract hydrogen peroxide, lipid hydroperoxides or xenobiotics, primarily as glutathione peroxidase or glutathione- Cofactor for enzymes such as S-transferase (GST). Moreover, increasing mGSH levels can improve different pathological environments such as hypoxia, ischemia/reperfusion injury, aging, liver disease, and neurological disease.
Part.2
In 2023, foreign researchers published an article in Vitamins and Hormones. Describes the essential antioxidant effects of reduced glutathione in mammalian cells.

Reduced glutathione (GSH) is an essential non-enzymatic antioxidant in mammalian cells. Glutathione can act directly as an antioxidant, protecting cells from free radicals and pro-oxidants, and as an antioxidant and detoxifying enzyme (such as glutathione peroxidase, glutathione S-transferase and glyoxalase) cofactor. Glutathione peroxidase detoxifies peroxides through a reaction coupled with the oxidation of glutathione to glutathione disulfide (GSSG). GSSG is converted back to GSH by glutathione reductase and the cofactor NADPH. Glutathione (GSH) can regenerate vitamin E after its detoxification reaction with lipid peroxyl radicals (LOO·). Glutathione is a cofactor of GST in the detoxification of electrophilic and xenobiotic substances. Methylglyoxal and glyoxal-induced dicarbonyl stress are alleviated by glyoxalase and glutathione. GSH regulates redox signaling through reversible oxidation of key protein cysteine residues via S-glutathionylation. Glutathiolamide is involved in other cellular processes such as protein folding, protection of protein thiols from oxidation and cross-linking, disulfide bonded protein degradation, cell cycle regulation and proliferation, ascorbate metabolism, apoptosis and ferroptosis.
Post time: Jan-14-2024


