Glutathione (GSH) is a tripeptide containing γ-amide bonds and sulfhydryl groups. It is composed of glutamic acid, cysteamine and glycine. It is widely distributed in mammalian, plant and microbial cells and is the most important The most abundant low molecular weight peptide containing sulfhydryl groups.
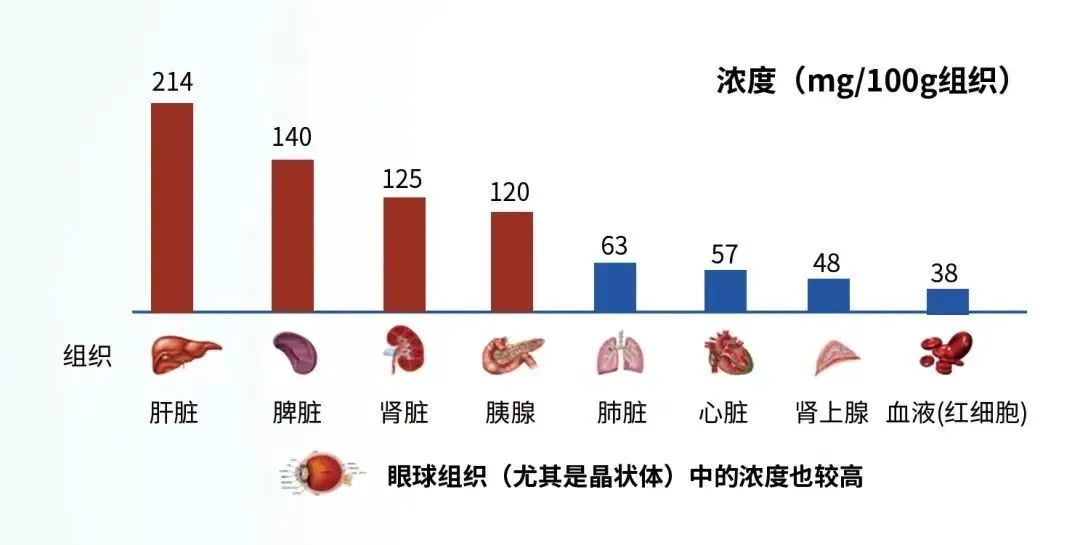
The sulfhydryl group on cysteine is the active group of glutathione, which is easy to combine with certain drugs (such as paracetamol), toxins (such as free radicals, iodoacetic acid, mustard gas, lead, mercury, arsenic and other heavy metals), etc., and has Integrate detoxification. Therefore, glutathione (especially glutathione in liver cells) can participate in biotransformation, thereby converting harmful poisons in the body into harmless substances and excreted from the body. Glutathione, which has the highest content in the liver, not only helps the liver detoxify, but also plays a certain protective role in the liver.
Reduced glutathione for the treatment of viral hepatitis
In 2017, researchers from the Department of Infectious Diseases of Pizhou People's Hospital of Jiangsu Province published a study in "Chinese and Foreign Medicine" on the clinical significance of reduced glutathione in the treatment of viral hepatitis. A total of 116 patients with viral hepatitis were enrolled in the study. Randomly divide into two groups. The conventional group was treated with conventional antiviral drugs and liver-protecting drugs, while the intervention group was treated with reduced glutathione on the basis of the conventional group. Compare the total effective rate of viral hepatitis treatment between the two groups of patients; the time when the therapeutic effect reaches significant effect; and the differences in liver function-related index values before and after treatment.
Research data shows that the total effective rate of viral hepatitis treatment for patients in the intervention group is 96.55% higher than that of the conventional group, which is 87.50%. The time for the intervention group to reach significant effect is shorter (17.51±1.41) days than the conventional group (27.39±2.77) days. The trough after treatment is The improvement in liver function-related index values was greater in the thione group.
The results show that the clinical application effect of reduced glutathione in the treatment of viral hepatitis is accurate, and it can effectively improve the clinical symptoms of patients, promote the recovery of their liver function, and shorten the treatment time.
Reduced glutathione for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B

In 2009, researchers from the Department of Infectious Diseases of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University and the First Hospital of Nanchang published a study in the "Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy" on the effectiveness of reduced glutathione tablets in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Observational studies. The researchers randomly divided 210 patients with chronic hepatitis B into treatment groups A to F and a control group, with 30 cases in each group. Treatment group A was given reduced glutathione tablets 0.2gtid, treatment group B was given reduced glutathione tablets 0.4gtid, treatment group C was given Weigan Futai tablets 1.2gtid, and treatment group D was given reduced glutathione tablets 0.4gtid. Thione tablets 0.2gtid + Weiganfutai tablets 1.2gtid. Treatment group E was given reduced glutathione tablets 0.4gtid + Weiganfutai tablets 1.2gtid. Group F was given reduced glutathione injection 1.2g+ Diammonium glycyrrhizinate injection 150mg, intravenous drip, the control group was given basic treatment such as vitamin C tablets 100mgtid, inosine tablets 200mgtid. All groups were treated for 14 days, and changes in symptoms, signs and liver function before and after treatment were observed.
Research data shows that the efficacy of all treatment groups is significantly better than that of the control group; the efficacy of treatment groups B and D is better than that of treatment group A, and the efficacy of treatment group E is better than that of treatment group B; treatment group A and treatment group C, treatment There was no significant difference between group E and treatment group F.
The results show that using a small dose of 0.2gtid can achieve the same effect as oral enzyme-lowering and liver-protecting drugs such as Weigan Futai. If a larger dose of 0.4gtid is used or combined with enzyme-lowering and liver-protecting oral drugs such as Weigan Futai, it can achieve the same effect. Achieve better results, and when used in combination, the effect is equivalent to that of reduced glutathione injection combined with diammonium glycyrrhizinate injection. Reduced glutathione tablets are very effective in treating chronic hepatitis B.
Reduced glutathione for the treatment of alcoholic liver disease

In 2016, researchers from the Second People's Hospital of Lanzhou City, Gansu Province published a study in "Clinical Medical Research and Practice", studying the effect of reduced glutathione treatment on patients with chronic viral hepatitis combined with alcoholic liver damage. . The researchers divided 90 patients with chronic viral hepatitis combined with alcoholic liver damage into two groups. The control group (40 cases) was treated with conventional symptomatic treatment, and the research group (50 cases) was treated with reduced glutathione on the basis of the control group. The clinical effects, adverse reactions, and changes in serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and total bilirubin (TBIL) contents of the two groups of patients before and after treatment were observed.
Research data shows that the total effective rate is 90.00%, which is significantly higher than the 77.50% in the control group. There is no significant difference in the serum ALT, AST, and TBIL levels of the two groups of patients before treatment. After treatment, the above indicators of the two groups of patients are higher than before treatment. There was a significant decrease, and the glutathione group was significantly lower than the control group.
The results show that the treatment of chronic viral hepatitis combined with alcoholic liver damage using reduced glutathione has a significant effect, high safety, and can better improve serum related indicators.
Post time: Dec-13-2023


