During astronauts' missions to space, the astronauts' DNA in their bodies is damaged due to cosmic radiation, and after astronauts experience space flight, their bones will become very fragile and more likely to fracture. Studies have shown that after a four-year journey through the universe, high-energy particles in space will cause 5% of the body’s cells to die and cause significant aging. Therefore, researchers are constantly looking for new ways to restore astronauts' bodies.

NMN and DNA
NMN improves DNA repair ability
Research published by Professor David Sinclair's team at Harvard Medical School in March 2017 in "Sciences" showed that by continuously intraperitoneally injecting NAD+ precursor NMN into elderly mice, PARP1 was found in elderly mice and mice treated with radiation. Enzyme activity has been significantly improved, blood white blood cell count, lymphocytes and hemoglobin have also been significantly increased, and DNA repair function has been significantly improved.

NMN and NASA
NMN is radiation resistant and prevents bone loss
In 2017, NASA took the lead in using NMN to help astronauts resist radiation and recover their bodies, making NMN the "armor" of astronauts.
In 2020, on the basis of confirming NMN's anti-aging ability, scientists also confirmed that NMN can resist radiation and prevent bone loss, and received an award from NASA.
NMN and bones
NMN can improve bone density
In May 2023, the research team of Xi'an Jiaotong University published relevant research in the international scientific journal "Cell Stress & Chaperones". Research shows that NMN can restore bone mineral density, an indicator of improved bone strength, in animal models of spaceflight microgravity. At the same time, NMN can also reduce bone-damaging oxidative stress.

1. In a simulated weightlessness environment, the level of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), an essential longevity factor in bones, decreases. NMN supplementation can restore NAD+ in bones.
To simulate how spaceflight affects bones, the team used a method used by NASA researchers—hindlimb deloading (suspending the rat so that its hind limbs do not touch the ground).
The research team measured bone NAD+ levels to study the subcellular mechanisms behind NMN's effect on improving osteopenia. The space rat model showed a significant reduction in bone NAD+, while NMN significantly restored bone NAD+ in the model. This suggests that NMN's ability to maintain bone density stems from its ability to increase NAD+ levels
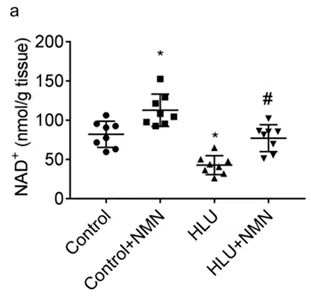
2. NMN can improve the bone density of osteopenic rats in a weightless environment.
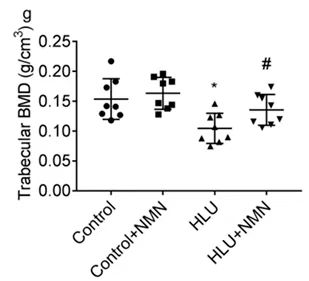
Bone mineral density is a sign of the strength of the bone structure. The researchers recorded bone mineral density data on bone-deficient rats.
The data found that rats that received hindlimb unloading for 4 weeks showed significantly lower bone mineral density, indicating osteopenia and concomitant bone fragility in the rats. However, when NMN was injected into the abdomen every three days, the rats' bone mineral density showed a tendency to recover. This also shows that NMN can rescue osteoporosis in a simulated space gravity environment.
3. Malondialdehyde, a marker of oxidative stress, is higher in the bones of animal models under simulated weightlessness. NMN can normalize this cellular stress marker.
Because oxidative stress is associated with bone degradation and osteopenia during spaceflight, the research team measured malondialdehyde, a molecular marker of oxidative stress.
The results found that after 4 weeks of simulated weightlessness, the rats' malondialdehyde levels more than doubled, and NMN reduced the surge in malondialdehyde. These results indicate that NMN promotes the activity of sirtuins proteins by increasing NAD+ levels, thereby removing oxidative stress factors and reducing oxidative stress to normal levels, which helps maintain bone density.
Summary
NMN
1. In a simulated weightlessness environment, the level of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), an essential longevity factor in bones, decreases. NMN supplementation can restore NAD+ in bones.
2. NMN can improve the bone density of osteopenic rats in a weightless environment.
3. Malondialdehyde, a marker of oxidative stress, is higher in the bones of animal models under simulated weightlessness. NMN can normalize this cellular stress marker.
NMN has shown good bone protection capabilities in animal model tests. This finding provides new evidence for the application of NMN in the treatment of osteoporosis and the physical recovery of astronauts; it also provides a basis for future clinical research on NMN in humans. .
The safety of NMN has been widely recognized by scientists from various countries, and it has shown good anti-aging and improvement of fatigue, sleep, exercise and other abilities. Now, the application research of NMN on astronauts has been further recognized, showing good potential for aerospace applications.

Post time: Jan-06-2024


