Naringin 15%
Naringin is a dihydroflavonoid compound. Since there is no conjugation between the A ring and the B ring, there is a strong ultraviolet absorption peak at 282nm, which makes naringin show a variety of biological activities and pharmacological effects. It has anti-inflammatory, antiviral, anti-cancer, anti-mutagenic, anti-allergic, anti-ulcer, analgesic, and hypotensive activities, can lower blood cholesterol, reduce the formation of thrombus, improve local microcirculation and nutrient supply, and can be used in the production of prevention and treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
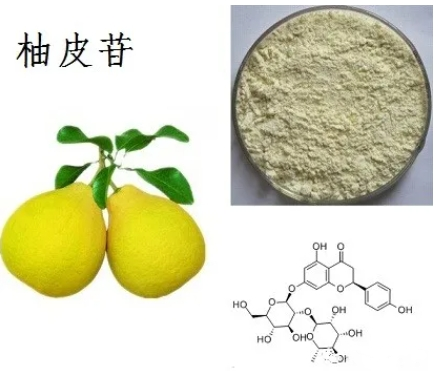
Basic information
▶CAS number: 10236-47-2
▶Molecular formula: C27H32O14
▶Molecular weight: 580.53
▶Properties: light yellow powder
▶Source: Fruit of Citrus paradisi Macfadyen
Pharmacological effects
1. Reports show that subcutaneous injection of 100mg/kg naringin in rats has a significant anti-inflammatory effect, and 200mg/l concentration of naringin has a strong inhibitory effect on vesicular stomatitis virus;
2. Reduce blood viscosity, reduce thrombus formation, and have analgesic, sedative and strong increase in bile secretion in experimental animals;
3. It has the properties of desensitization and anti-allergy, blood circulation and spasm relief, improvement of local microcirculation and nutrient supply, and has a unique therapeutic effect on promoting drug excretion, relieving streptomycin damage to the 8th cranial nerve, and relieving the toxic and side effects of streptomycin;
4. Under alkaline conditions, naringin can be oxidized to obtain dihydrochalcone sweetener, which is 1000 times sweeter than sucrose. Naringin reacts with isovanillin to obtain neohesperidin, which is 950 times sweeter than dihydrochalcone and is a new generation of non-toxic, low-energy, high-sweetness sweetener.
Application
1. Application of naringin in medicine
Naringin shows a variety of biological activities and pharmacological effects. Naringin has the effect of lowering cholesterol, mainly by inhibiting the activity of cholesterol synthase in the body, reducing the synthesis of cholesterol in the body, promoting the decomposition of cholesterol, and reducing low-density lipoprotein in the body. When naringin is added to toothpaste, the results of pharmacological tests show that the new toothpaste containing the natural plant active ingredient naringin has good anti-inflammatory and hemostatic effects, and the acute toxicity test also shows that naringin is safe. At the same time, the stability study of naringin in toothpaste shows that the quality of naringin added to toothpaste as an effective ingredient is stable and controllable. In addition, naringin is also widely used in medical research fields such as blood, bone cells, and muscle cells.
2. Application of naringin in food science
Naringin can be widely used in food science as a natural antioxidant. Naringin was selected as a natural antioxidant for pork. The study found that naringin has a significant effect on improving the brightness and yellowness of meat, and the effect on the redness of meat first decreases and then rises. Considering the globulin precipitation reaction and freshness sensory indicators, 5g/kg of naringin should be selected as a natural antioxidant and preservative for animal meat such as pork, and the effect is more significant. However, naringin usually has a certain hydrophilicity, which affects its use as a natural antioxidant. Naringin is modified, and a fat chain is introduced into its molecule through a lipase-catalyzed esterification reaction, which greatly reduces its hydrophilicity.
3. Application of naringin in chemistry
Naringin is also widely used in chemical synthesis as an important raw material. Molecular imprinting membranes have attracted more and more attention since the early 1990s because of their dual advantages of molecular specific recognition and membrane separation. Using naringin as a template molecule and chitosan as a membrane material, a water-phase recognition naringin molecular imprinting chitosan membrane was prepared in an aqueous phase by sulfuric acid crosslinking. In addition, naringin can also be hydrolyzed into important biopharmaceutical and chemical intermediates such as (glycoside) (Naringenin -7 -O -glucoside), (naringenin), (L-rhamnose), and (Glu-cose).
Article Written By: Coco Wang
Post time: Mar-14-2024


