Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) as an anti-aging health product – Promises and safety concerns
This article was published in Journal of Advanced Research
Volume 37, March 2022, Pages 267-278
The successful control of communicable diseases in the 20th century led to a sharp rise in the mean life expectancy of many countries. In 2019, number of persons, aged 65 or over was 702.9 million in the world and it is projected to be 1548.9 million by 2050. Percentage of global population aged 65 years or over in 2019 and future projections according to the medium-variant projection is illustrated in Fig. 1. Along with increasing elderly population, the prevalence of age-related diseases such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, osteoarthritis, neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, diabetes mellitus and cancers has gone up leading to heavy global socioeconomic and medical burden.
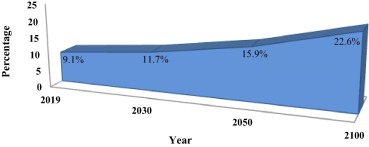
Fig. 1. Percentage of global population aged 65 years or over according to the medium-variant projection (UN, 2019).
Therefore, age management medical practices have been mushrooming in the world for recommending nutritional supplements, various drugs, exercise programs, hormone therapies and other treatments to mitigate the effect of aging. Consequently, the consumer demand and the global market value for anti-aging health products are on the rise . Excessive demand of consumers and high profit margin for manufacturers are the major driving force behind the release of anti-aging health products without adequate safety testing . Thus, careful comprehensive and stepwise scientific preclinical and clinical investigations are crucial to be conducted.
Among various anti-aging health products, nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has been gaining an increasing attention as a promising anti-aging product. The mitochondrial decay, which is responsible for aging, can be reversed by the increased levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) in the body. NMN is a precursor of NAD+ that acts as an intermediate in NAD+ biosynthesis, while dietary supplements of NMN are found to increase the NAD+ levels in the body . NMN is a bioactive nucleotide formed by the reaction between a nucleoside comprising nicotinamide and ribose and a phosphate group . It naturally presents in a variety of plant and animal food sources. Furthermore, several studies have been carried out to investigate the potential of biotechnological production and purifying NMN from bacterial and yeasts .
Other than anti-aging potential of NMN, a wide range of pharmacological activities have been identified in a number of in vivo studies. The link between NMN and the incidence of Alzheimer’s disease, obesity and associated complications, cerebral and cardiac ischemia, and age- and diet-induced type 2 diabetes has been studied extensively . Though, previous attention of scientific community has been paid on NMN only as an intermediate in NAD+ biosynthesis, recently, a number of pharmacological activities triggered by increasing NAD+ levels in the body, especially anti-aging activity have been taken the centre of attention. As a result, a number of studies including cell culture, animal models and human clinical trials have been conducted to investigate the promises and the safety concerns of using NMN as an anti-aging health product and the potential of using NMN as a supplement to avoid age-related disease conditions. Hence, this review intends to present the most recent advances and current knowledge on promises and safety concerns of the use of NMN as an anti-aging health product, its other pharmacological and therapeutic uses and mechanism of action underlying the anti-aging properties with an interest to stimulate further research and offer an insight to the possibility of translating successful preclinical and clinical anti-aging outcomes of NMN into an effective treatment of aging and age-related diseases.
Post time: Dec-04-2023


