Glutathione is divided into food grade, cosmetic grade, health care grade and pharmaceutical grade. When it comes to glutathione, many people will feel familiar because it appears in many aspects of people’s daily lives. So what exactly is glutathione?
1.What is glutathione
Glutathione (GSH) is a tripeptide containing a γ-amide bond and a sulfhydryl group. It is composed of glutamate, cysteamine, and glycine. It is widely distributed in mammalian, plant and microbial cells and is the most important and abundant low molecular weight peptide containing sulfhydryl groups.
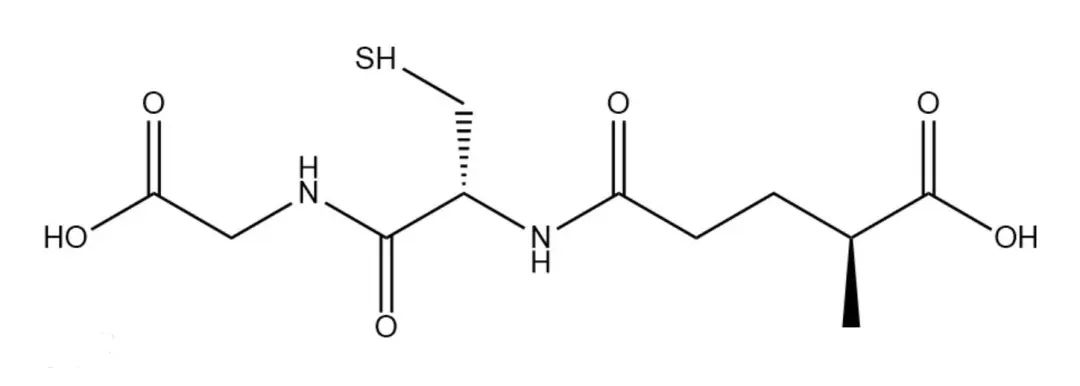
Glutathione comes in two forms: reduced and oxidized. Among them, active reduced glutathione is the main form under physiological conditions. These two forms can be converted into each other catalytically by glutathione reductase.
2. Synthesis method of glutathione
In 1888, De Rey-Pailhade isolated natural GSH from yeast for the first time. In 1921, Hopkins prepared GSH crystals for the first time. In 1929, Pirie and Pinhey obtained the correct structural formula of GSH through physiological and chemical studies on tripeptides. In 1935, Hanington synthesized GSH for the first time. With the continuous in-depth research of glutathione by scientists and the rapid development of modern technology, the main preparation methods of glutathione today are: chemical synthesis, biological fermentation and biological enzymatic methods.
1.Chemical synthesis method
Reduced glutathione is highly active and versatile. The active ingredients are difficult to isolate and require many chemical steps to do so. Therefore, the purity of reduced glutathione products produced by chemical methods is not high, and the overall yield is not high.
2. Biological fermentation method

Biological fermentation has been developed for a long time and the process is mature, but the production cycle is long and some by-products are produced. The process control is complex, the technical requirements are high, and the output is low, which is not conducive to industrial large-scale production.
3. Biological enzymatic method

The enzymatic production cycle is short, the yield is high, it is relatively easy to purify, and the cost is low. And the enzymatic method is more environmentally friendly. It is the main method of industrial scale production at present.
3.Efficacy of glutathione
Glutathione (GSH), as an important intracellular metabolic substance, is a sulfhydryl-containing tripeptide composed of glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine; it is also an auxiliary enzyme of glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase. It is a coenzyme of glyoxalase and triose dehydrogenase, participates in the tricarboxylic acid cycle and sugar metabolism in the body, and has antioxidant and comprehensive detoxification effects. Glutathione also helps maintain normal immune system function.
1. Detoxification
The sulfhydryl group on cysteine is the active group of glutathione and is easily combined with certain drugs (such as paracetamol) and toxins (such as free radicals, iodoacetic acid, mustard gas, lead, mercury, arsenic and other heavy metals). ), etc., and has a comprehensive detoxification effect. Therefore, glutathione (especially glutathione in liver cells) can participate in biotransformation, thereby converting harmful poisons in the body into harmless substances and excreted from the body. And glutathione has a protective effect on leukopenia caused by radiation, radioactive drugs or anti-tumor drugs.
2. Antioxidants
Glutathione can activate a variety of enzymes, such as sulfhydryl (SH) enzyme coenzyme, etc., thus promoting the metabolism of sugar, fat and protein. The active sulfhydryl group (-SH) of GSH is the most important functional group. It can participate in a variety of important biochemical reactions in the body, protect the sulfhydryl groups of important enzyme proteins in the body from oxidation and inactivation, and ensure energy metabolism and cell utilization. At the same time, it combines with free radicals in the body through sulfhydryl groups and can directly reduce free radicals into acidic substances, thereby accelerating the excretion of free radicals and combating the damage of free radicals to important organs. Even the decrease in GSH content is a potential early activation signal of apoptosis, and the subsequent generation of oxygen free radicals promotes apoptosis.
3. Protect the immune system
Activated T cells produce reactive oxygen species (ROS), triggering the antioxidant glutathione (GSH) response, which is necessary to buffer ROS rise and prevent cell damage. The antioxidant GSH pathway plays an important role in metabolic integration and reprogramming of T cell effectors during inflammatory T cell responses. Therefore, GSH prevents autoimmune diseases by affecting T cell-specific ablation and blocking antiviral defenses.
4. Application of glutathione
As an important regulatory substance in cells, glutathione has multiple effects and levels and is used in many aspects of life.
1.Clinical drugs
Liver damage: viral liver disease, drug-induced liver disease, toxic liver damage, fatty liver, cirrhosis, etc.;
Kidney injury: acute drug-induced kidney injury, uremia;
Protection from radiotherapy and chemotherapy;
Diabetes: complications, neuropathy;
Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy; various types of hypoxemia.
2. Healthcare applications
Whitening and antioxidant, regulating skin tone, detoxifying and protecting liver, improving immunity, anti-aging, etc.
3. Food additive
Added to flour products, it can have a reducing effect. The time for making bread is shortened to about one-third of the original time, and it also plays a role in enhancing food nutrition and other functions.
When added to yogurt and baby food, it is equivalent to vitamin C and acts as a stabilizer.
Added to meat products, cheese and other foods, it can enhance flavor and preserve freshness.
Post time: Nov-11-2023


