
Currently, commonly used methods for extracting plant extracts include: solvent extraction, ultrasonic extraction, microwave extraction and enzyme extraction;
1. Solvent extraction
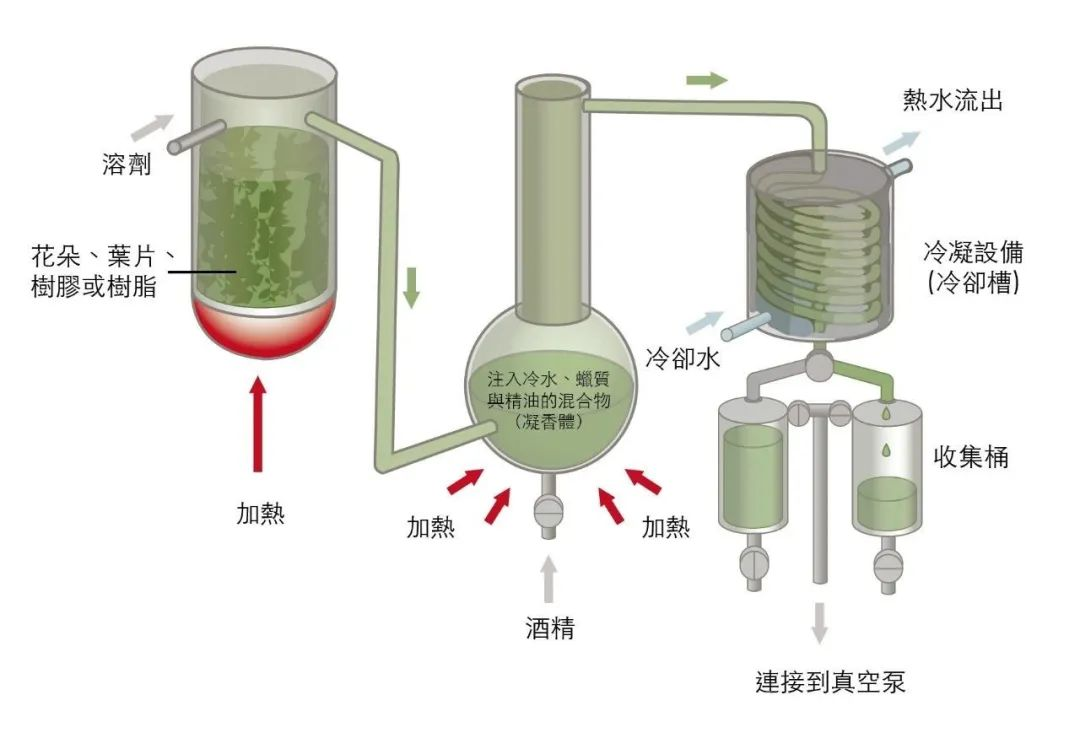
The solvent extraction method uses a solvent to extract active ingredients from solid raw materials. The solvent used must be mutually soluble with the extracted solute. Crush the plant raw materials, put them into a suitable container, add several times the solvent, and extract them through soaking, percolation, decoction, reflux and continuous extraction.
During the solvent extraction process, the concentration of the solvent, solid-liquid ratio, extraction temperature and extraction time will directly affect the extraction rate of active ingredients. Cristina Juan et al. used solvent extraction to extract ochratoxin A from rice, and used fluorescence detection and liquid chromatography to determine the OTA content. The results show that under appropriate material-to-liquid ratio, extraction temperature and extraction time, the OTA content in the extract is 4.17ng/g. Monte D. Holt et al. used solvent extraction to extract alkylresorcinols from raw and cooked wheat seeds. Experiments show that solvent extraction can save extraction time.
2.Ultrasonic extraction
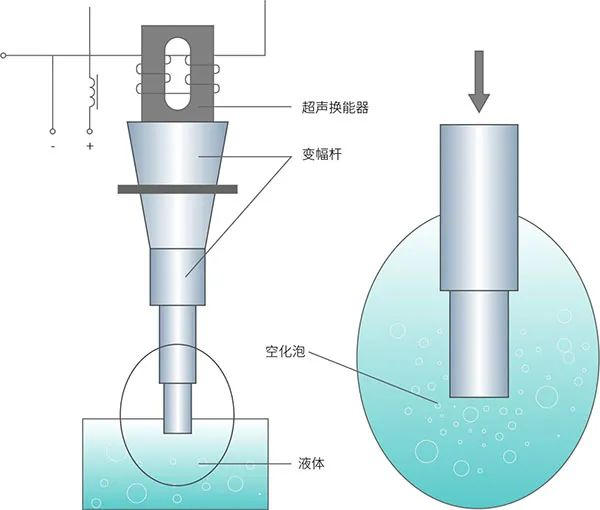
Ultrasonic extraction uses the strong vibration and null effect generated by ultrasonic waves to accelerate the release, diffusion and dissolution of substances in plant cells into the solvent, while keeping the structure and biological activity of the extracted substances unchanged.
The principle of ultrasonic extraction is mainly a physical process, and it is a relatively new extraction method that has received more and more attention in recent years. For most components, compared with conventional solvent extraction, ultrasonic extraction can greatly shorten the extraction time, consume less solvent, and have a high extraction rate, so it has higher extraction efficiency.
During the ultrasonic extraction process, the selection and concentration of the solvent, solid-liquid ratio, extraction temperature and extraction time will directly affect the extraction rate. Zhou Ling et al. used ultrasonic waves to extract Schisandra chinensis and mainly studied the influencing factors of ultrasonic extraction rate.
Experimental results show that the extraction rate increases with increasing temperature and power. Hong Le et al. used ultrasonic waves to extract vitamin E and phenolic compounds from cherries, mainly comparing the differences in extraction time and extraction rate between ultrasonic extraction and enzyme extraction. Experimental results show that ultrasonic extraction time is 6 times shorter than enzymatic extraction time, and the extraction rate is 2 to 3 times that of enzymatic extraction. Zhong et al. used ultrasonic waves to extract chlorophyll from fresh bamboo leaves, and used a spectrophotometer to quantitatively measure the extracted chlorophyll content. The results show that compared with the ordinary organic solvent extraction method, the ultrasonic extraction method not only has a high extraction rate, fast speed and high efficiency, but also can be extracted at room temperature without heating, saving energy.
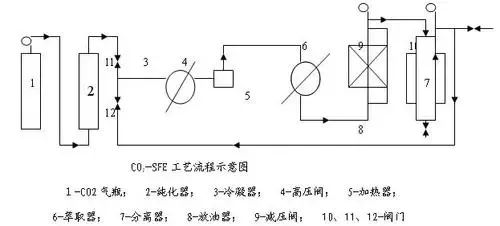
3.Supercritical fluid extraction
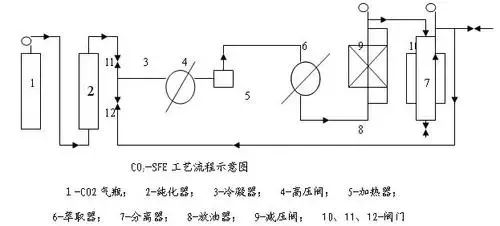
Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) is a newer extraction separation technology that usually uses CO2 as the extraction agent.
The principle of supercritical fluid extraction is to take advantage of the unique solubility of supercritical fluids and the fact that the solubility of substances in supercritical fluids is very sensitive to changes in pressure and temperature. By increasing the temperature and reducing the pressure (or both ) method to separate substances dissolved in supercritical fluids to achieve the purpose of separation and purification. It has two functions of distillation and extraction, and has the advantages of difficult deactivation of active ingredients, high product quality, and simultaneous completion of extraction and separation. It is considered a green and environmentally friendly high-tech separation technology, especially suitable for unstable conditions.
In the mid-1980s, supercritical CO2 extraction technology was gradually applied to the extraction and separation of plant active ingredients. It is a relatively successful new technology in research and application. Xu Ruiqi and others used CO2 and ethanol as solvents to extract the active ingredients of Ganoderma lucidum using supercritical fluid extraction. The results show that supercritical fluid extraction ensures the fluidity of Ganoderma lucidum extract and is not affected by temperature. Monica Waldeb.ck et al. used pressurized fluid extraction technology to extract squalene and -tocopherol from olives. Experimental results show that when the solvent is ethanol, the extraction temperature is 190°C, and the extraction time is 10 minutes, the extraction effect is better. Zianger et al. used supercritical CO2 extraction technology to extract natural vitamin E from wheat germ, and mainly studied the effects of pretreatment and extraction conditions on the yield. Experimental results show that when the particle size is 30 mesh, the pressure is 4000-5000 psi, the extraction temperature is 40-50°C, and the CO2 fluid flow rate is 2.0mL/min, the extraction rate is higher.
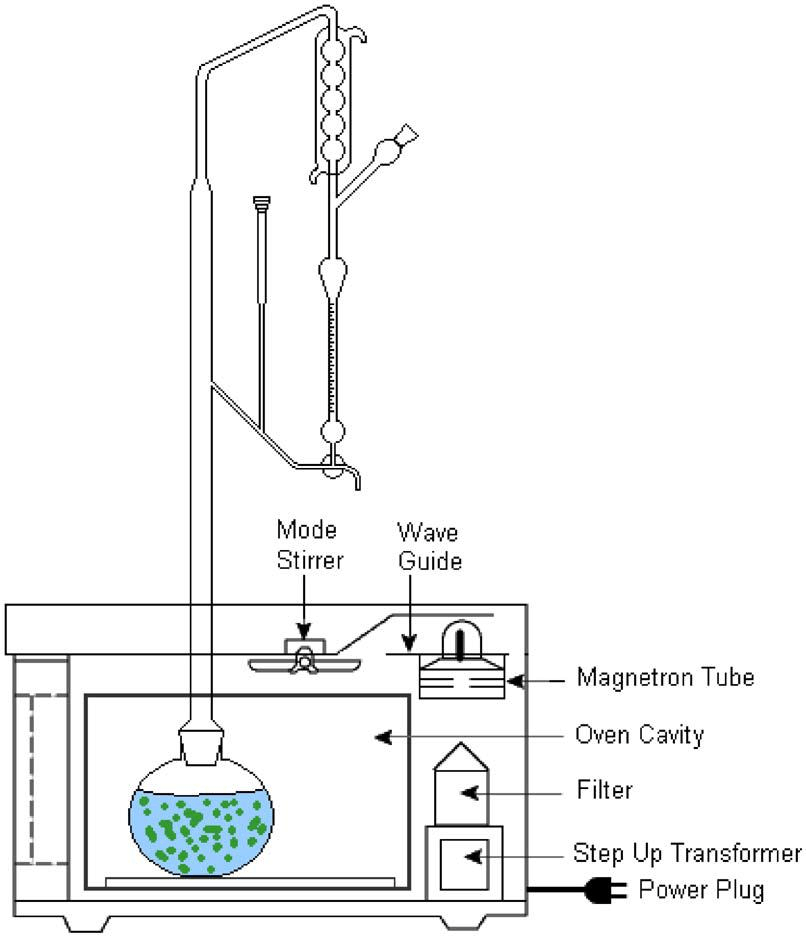
4.Microwave-assisted extraction method
Microwave is a type of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation. The polar molecules of the irradiated material quickly turn and orient in the microwave electromagnetic field, causing tearing and mutual friction, which can ensure the rapid transmission and full utilization of energy, and has the advantages of energy saving and no industrial pollution. However, the penetration depth of microwave is limited (in the same order of magnitude as its wavelength), and the mass transfer effect is not obvious during the enhanced extraction process.
Ultrasonic wave is a high-frequency mechanical wave with turbulence effect, disturbance effect, interface effect and energy concentration effect. The thermal effect generated by ultrasonic waves is not obvious and is limited to a small range around the air bubbles. Combining them together, the synergistic effect is beneficial to the release of wall-breaking ingredients, etc. That is, using microwave-ultrasonic synergistically enhanced extraction technology, a cheap, pollution-free method for extracting biologically active substances can be obtained.
HeJT et al. used microwave-ultrasonic fields to extract water-soluble bioactive ingredients in traditional Chinese medicine and achieved good results. Luo Feng et al. Microwave-ultrasonic synergistic extraction of licorice flavonoids. Ma Lihua et al. studied the effects of traditional distillation and microwave-ultrasonic collaborative extraction on the extraction rate of carotenoids in burdock, and determined better extraction conditions through orthogonal experiments. Bai Jin et al. used anhydrous ethanol-distilled water and anhydrous ethanol-distilled water (volume ratio 1:1) as solvents, used microwave and ultrasonic waves to extract aloe vera, and used an edible oil oxidation stability tester to measure the effects of the extract on rapeseed oil, pig Antioxidant effects of oil, cottonseed oil and sunflower seed oil.
5.Enzyme extraction method
The cell wall of natural plants is composed of cellulose, and the active ingredients of the plant are often wrapped in the cell wall. The enzyme extraction method is a method that uses cellulase, pectinase, protease, etc. (mainly cellulase) to destroy the cell wall of the plant to maximize the dissolution and separation of the plant's active ingredients. In the extraction process of enzymatic extraction method, the selection of enzyme, enzyme concentration, pH value, enzymatic hydrolysis temperature, and enzymatic hydrolysis time will all affect the extraction rate of plant extracts.
E.BARZANA et al. used enzyme extraction method to extract carotenoids from marigold. They mainly studied the effects of material-liquid ratio, enzyme concentration, enzymatic hydrolysis time and temperature on the extraction rate. The research results showed that the optimal extraction process is: material-liquid ratio The ratio is 1:4, the enzyme concentration is 0.3%, the extraction time is 1.5h, and the temperature is 25℃. Zhang Xiaoqing et al. used an enzyme extraction method to extract flavonoids, the active ingredient in Ginkgo biloba, and used orthogonal experiments to find the optimal process conditions that affect the extraction rate, such as enzyme concentration, pH value, enzymatic hydrolysis temperature and time.
Post time: Jan-25-2024


